CHAPTER 4
MEASURING THE SUCCESS OF STRATEGIC INITIATIVES
Measuring Information Technology's Success
Efficiency and Effectiveness
Benchmarking - Baseline Metrics
Benchmarking – a process of continuously measuring system results, comparing those results to optimal system performance (benchmark values), and identifying steps and producers to improve system performance.
The Interrelationship of Efficiency and Effectiveness IT Metrics
Common types of efficiency IT metric;
Common types of effectiveness IT metrics
- Key performance indicator – measures that are tied to business drivers.
- Metrics are detailed measures that feed KPIs.
- Performance metrics fall into the nebulous area of business intelligence that is neither technology, nor business centered, but requires input from both IT and business professionals.
Efficiency and Effectiveness
- Efficiency IT metric – measures the performance of the IT system itself including throughput, speed, and availability.
- Effectiveness IT metric – measures the impact IT has on business processes and activities including customer satisfaction, conversion rates, and sell-through increases.
Benchmarking - Baseline Metrics
Benchmarking – a process of continuously measuring system results, comparing those results to optimal system performance (benchmark values), and identifying steps and producers to improve system performance.
The Interrelationship of Efficiency and Effectiveness IT Metrics
Common types of efficiency IT metric;
- Throughput - the amount of information that can travel through a system at any point.
- Transaction speed - the amount of time a system takes to perform a transaction.
- System availability - the number of hours a system is available for users.
- Information accuracy - the extent to which a system generates the correct results when executing the same transaction numerous times.
- Web traffic - includes a host of benchmarks such as the number of page views, the number of unique visitors, and the average time spent viewing a Web page.
- Response time - the time it takes to respond to user interactions such as a mouse click.
Common types of effectiveness IT metrics
- Usability - The ease with which people perform transactions and/or find information. A popular usability metric on the Internet is degrees of freedom, which measures the number of clicks required to find desired information.
- Customer satisfaction - Measured by such benchmarks as satisfaction surveys, percentage of existing customers retained, and increases in revenue dollars per customer.
- Conversion rates - The number of customers an organization “touches” for the first time and persuades to purchase its products or services. This is a popular metric for evaluating the effectiveness of banner, pop-up, and pop-under ads on the Internet.
- Financial - Such as return on investment (the earning power of an organization’s assets), cost-benefit analysis (the comparison of projected revenues and costs including development, maintenance, fixed, and variable), and break-even analysis (the point at which constant revenues equal ongoing costs).
Interrelationships between efficiency and effectiveness.
Metrics for Strategic Initiatives
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Metrics
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Metrics
Business Process Re engineering (BPR) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Metrics
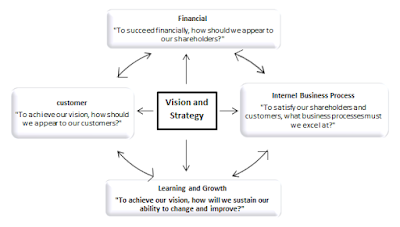
Balanced scorecard is a management system, in addition to a measurement system, that enables organizations to clarify their vision and strategy and translate them into action






Comments
Post a Comment